Inventory Management: A Comprehensive Understanding of Periodic and Perpetual Inventory
.png?alt=media)
A business’s ability to manage its inventory often determines its ability to grow, whether a wholesale store, manufacturing enterprise, or restaurant. This involves tracking all the goods and materials used in the business, ensuring that there are adequate quantities of everything. There are two primary types of inventory: periodic and perpetual. Both types have advantages and disadvantages, and a proper understanding of these concepts can help businesses achieve optimal profitability.
Concept of Inventory
Concept of Inventory
Inventory is a quantifying process that organizes and records all goods and products available in a company's warehouses at a given moment. This process is necessary for any business operation to control assets and ensure the ability to meet the demand for products and services. Inventory can include goods ready for sale, raw materials used in production, and unfinished goods. Businesses can reduce costs and increase efficiency and profitability by managing inventory effectively.
Categories of Inventory
There are three main types of inventory in any business operation: raw inventory, work-in-progress inventory, and finished inventory. Raw inventory includes the raw materials that have been purchased but not yet used in production. Work-in-progress inventory includes the materials that have already been used in the production process but have not yet been finished. Finally, the finished inventory contains the products that have been manufactured and are ready for sale.
The Importance of Inventory in Improving Operational Efficiency
Inventory management is a fundamental process and essential for any business. It helps determine the actual value of available assets, ensuring accurate financial reporting, protecting assets, and providing a clear picture of the company's financial health. Inventory management enhances operational efficiency by balancing supply and demand, reducing issues related to stock shortages or overstocking. It also helps identify discrepancies in quantities, preventing theft and waste. Additionally, it allows companies to identify damaged or expired goods and dispose of them safely. Finally, inventory management promotes legal compliance and financial transparency, boosting investor confidence, reducing legal risks, and supporting business continuity and growth.
Responsibilities of an Inventory Accountant
An inventory accountant plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of the inventory process. Their responsibilities include various financial and organizational tasks, such as:
- Preparing Inventory Records: Ensuring all data related to quantities and values is updated and correctly entered into the system, including updating records after every purchase, sale, or damage.
- Comparing Actual and Recorded Quantities: Matching recorded data with actual quantities in the warehouse to identify discrepancies or errors. If differences are found, the accountant analyzes the causes and takes corrective actions, such as recording losses or adjusting records.
- Valuing Inventory: Using methods like FIFO, LIFO, or weighted average, the accountant calculates the financial value of inventory, aiding in accurate financial reporting. This valuation directly impacts income statements and balance sheets.
- Preparing Reports and Analyses: Analyzing inventory data to identify trends, such as slow-moving items or those needing restocking. These reports assist management in making critical decisions about purchasing, pricing, and discounts.
- Ensuring Compliance with Accounting Standards: The accountant ensures all operations comply with local and international standards, such as IFRS or GAAP, ensuring financial transparency and reducing legal risks.
Periodic Inventory vs. Perpetual Inventory
In periodic inventory, inventory records are updated at the end of a particular period, which could be daily, weekly, monthly, or even yearly. Companies in this type of inventory have to conduct physical inventory audits to determine the amount of remaining goods.
On the other hand, in perpetual inventory, inventory records are updated in real time with every purchase or sale transaction. This type of inventory relies on information technology to accurately track goods and increase operational efficiency.
Challenges of Perpetual Inventory
Perpetual inventory, despite its numerous advantages, is not without challenges. Implementing it correctly requires using advanced technology to effectively track operations and accurately follow goods. These systems can be costly for small to medium-sized businesses trying to stay competitive in a market. In addition to the cost, dealing with inventory errors, theft, or damage in real-time can be difficult, especially in environments dealing with large quantities of goods. Perpetual inventory also requires continual system and software updates to maintain data accuracy, which can be a challenge for companies lacking the necessary resources.
Challenges of Periodic Inventory
The challenges associated with the periodic inventory system are several. First, periodic inventory may require a significant effort in certain cases, especially if the company is dealing with large quantities of goods. Periodic inventory may also result in business operations stopping during the inventory period, which can lead to financial losses. In addition, it can be difficult to detect errors and embezzlement in the inventory until the next periodic inventory is performed, exposing the company to the risk of loss.
Best Timings of Inventory Counts
The timing of inventory counts is as important as the process itself. Choosing the right time can significantly impact data accuracy and operational efficiency. Key times for conducting inventory counts include:
- End of the Financial Period. Whether monthly, quarterly, or annually, companies need accurate data to prepare financial reports and measure performance. Inventory counts at this stage help determine actual profits and losses.
- Before Budgeting or Purchasing Plans. Before deciding to purchase new goods or adjust production plans, companies need to know exactly what is available in stock. Inventory counts at this stage ensure no over-purchasing or shortages of raw materials.
- After Peak Seasons or Major Marketing Campaigns. After periods of high sales, such as holidays or seasonal discounts, actual quantities may differ from recorded ones due to the rapid movement of goods. Inventory counts at this stage help identify discrepancies or theft and provide accurate data for campaign performance analysis.
- Unexpected or Surprise Counts. Conducted when there is suspicion of inventory issues, such as theft or damage. Surprise counts can quickly reveal problems and help take immediate corrective actions.
- Before Changing Systems or Accounting Software. When transitioning to a new inventory management system, it is essential to ensure that the data entered is accurate. Inventory counts at this stage ensure the new system starts with reliable data.
Read more: Inventory Management: Techniques And Types Explained. EBITDA: Calculation, Meaning, And Traits.
Here is an example of what these transactions might look like in a real-world business context:
Purchasing Goods
If a business purchases goods to add to its inventory, the journal entry in its books might look like this:
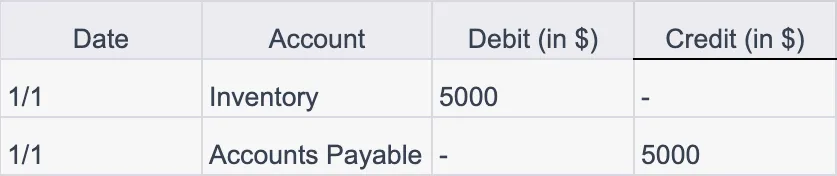
This entry signifies that $5000 worth of goods was added to inventory, and this amount is owed to suppliers (recorded as Accounts Payable).
Selling Goods
When the business sells goods, two transactions are generally recorded – one for the revenue from the sale, and another for the cost of the goods sold (COGS):
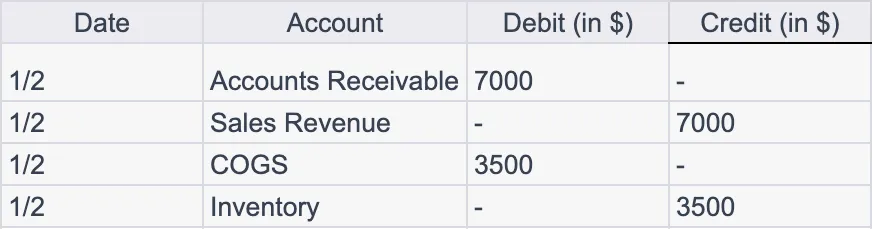
The first entry records the sales revenue that is expected to be received (Accounts Receivable), while the second entry records the COGS and decreases the Inventory.
Sales Returns
If a customer returns goods that were previously sold, the entries would look like this:
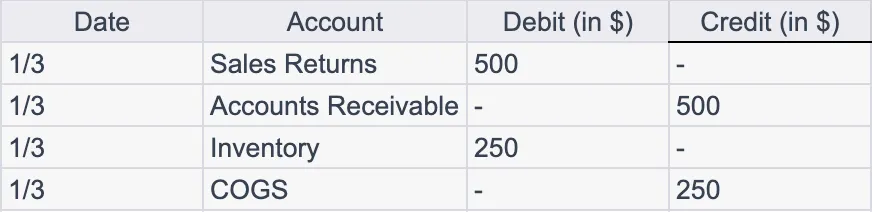
The Sales Returns account records the return of sales amount, reducing the Accounts Receivable. The second entry increases the Inventory for the returned goods and reduces the COGS.
Paying for Expenses
If the business incurs expenses related to the sale (like delivery charges), it might record:
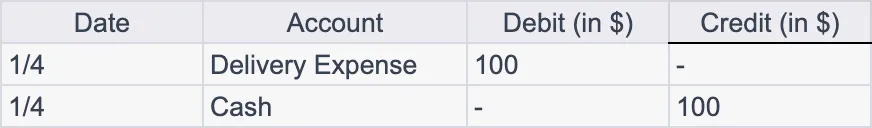
This entry increases the Delivery Expense account and decreases the Cash account.
Read more: Debit vs. Credit: Everything You Need to Know.
Inventory Ledger Inputs
An inventory ledger is a powerful tool that helps companies manage inventory effectively. It contains several key elements to ensure data accuracy and accessibility. Below is a table explaining these elements and their roles:
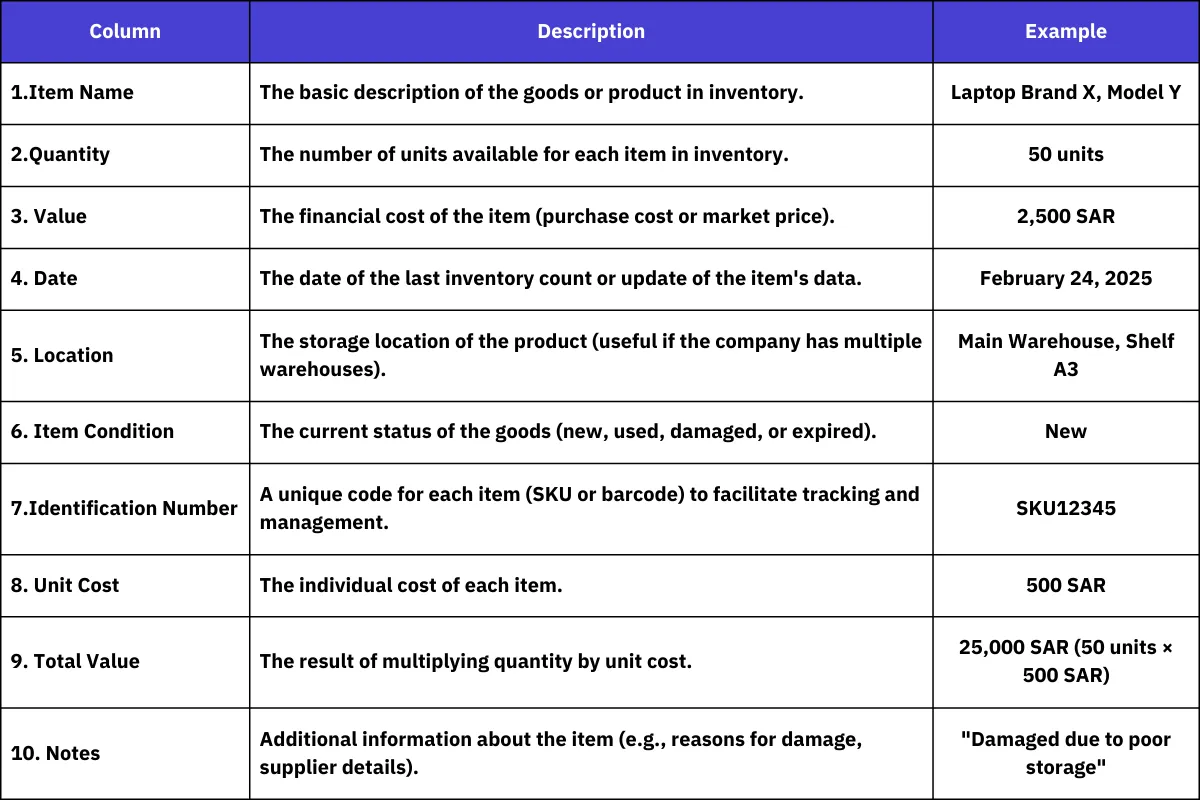
Best Practices for Inventory Management
Effective inventory management requires good planning, organization, and control. First, companies need to understand demand and its forecasts to ensure inventory aligns with demand. In addition, the right inventory management tools, such as inventory systems, should ensure continuous inventory updates and avoid inventory shortages or excesses. Lastly, companies should invest in workers training on the best inventory management practices to achieve the highest effectiveness in inventory operations.
How to Handle Damaged or Expired Inventory Items?
If damaged or expired items are neglected, they can inflate inventory value unrealistically, affecting financial reports and decision-making.
- Conduct Regular Inventory Checks: Perform comprehensive inventory checks to identify damaged or expired items, especially in industries that deal with perishable goods like food or pharmaceuticals.
- Establish Clear Policies: Once damaged or expired items are identified, establish clear policies for handling them, such as repairing damaged items or safely disposing of expired ones through recycling or specialized facilities.
- Record Losses in Financial Statements: Record the value of damaged or expired items as losses in financial accounts to maintain accurate financial data.
- Analyze the Impact: Analyze the impact of these losses on operational and financial performance to adjust purchasing policies or improve storage conditions. For example, if a large percentage of inventory is spoiled due to poor storage, the company may need to invest in improving storage infrastructure.
The Technological Role in Inventory Management: Using Software in Inventory Management
In the modern digital world, software has radically changed how to conduct inventory management.
- Software allows for instant tracking of current inventory and continuous data updates.
- Software provides detailed reports that aid in analyzing and improving inventory processes.
- Wafeq Accounting software not only allows for inventory tracking but also provides a powerful suite of tools that help companies maximize their inventory-related data.
- Companies can use sales analytics, profitability, and cost analytics to improve processes and increase efficiency.
Inventory and Profitability: The Relationship between Inventory Management and Profitability in Business.
Effective inventory management plays a crucial role in achieving profitability in business. It preserves financial resources by minimizing unnecessary inventory costs, such as excess storage costs and losses resulting from damaged or surplus products. Ensuring the availability of required products at the same time as demand can also improve customer satisfaction and increase sales. Businesses that manage their inventory well have a greater capacity to adapt to market changes and customer requirements, thereby increasing their profitability.
How to Calculate Net Profit After Annual Inventory?
- Calculate Total Revenue: The total amount earned from sales during the year.
- Deduct Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and any direct expenses related to producing the goods sold.
COGS can be calculated using the formula: COGS = Opening Inventory + Purchases - Closing Inventory.
COGS can be calculated using the formula: COGS = Opening Inventory + Purchases - Closing Inventory.
- Deduct Operating Expenses: Such as salaries, rent, and utilities, from gross profit (revenue minus COGS).
- Add or Deduct Other Income/Expenses: Such as interest or taxes, to arrive at net profit.
The final formula is:
The final formula is:
Net Profit = Total Revenue - COGS - Operating Expenses ± Other Income/Expenses.
How to Implement Inventory Management in Wafeq
Wafeq helps track inventory automatically during purchases or sales. To enable inventory tracking for a product, follow these steps:
- Go to the right menu and select "Products" to open the page.
- Enter product details:
- Enter the product name and SKU.
- Add a description to clarify the product's details.
3. Set Cost and Price (optional):
- Record the cost of the product's purchase, so Wafeq fills it in automatically when issuing a sales invoice.
- Add the selling price to use it as a default value when creating purchase invoices.
4. Enable Inventory Tracking: Mark "Yes" in the "Track Inventory" column to record available quantities automatically when issuing sales or purchase invoices.
5. Set Accounts and Taxes:
- Wafeq automatically adds the COGS account.
- Select the account for recording revenue and the income tax rate.
- Enter the purchase tax rate added to invoices each time you buy the product.
Quick Guidance:
Quick Guidance:
- Ensure product data is updated regularly to maintain inventory accuracy.
- Use unique descriptions and codes to simplify product searches.
Also Read: Inventory Turnover Ratio: Formulas, Examples, and KPIs.
Inventory management is a vitally important task for any business type. Properly managing inventory can provide companies with financial stability and the ability to predict profitability. However, it requires dedication and attention to detail, especially when dealing with large quantities of goods and multiple transactions. Using technology and software like Wafeq can help to simplify this process and make it more accurate and efficient. But even with the use of software, it's essential that the right individuals have the skills and knowledge necessary to manage inventory effectively. The challenges facing inventory management can be daunting, but with good practices and the right tools, companies can overcome these challenges and ensure that their warehouses operate efficiently and cost-effectively. Building an effective inventory system can help reduce expenses and increase profits, which benefits businesses in the long run.
FQAs about Periodic and Perpetual Inventory:
What is the Difference Between Physical and Accounting Inventory?
Physical inventory relies on the actual count of goods and products in stock by inspecting each item and recording actual quantities. Accounting inventory focuses on valuing and recording inventory in financial records using data such as purchase costs and COGS. It is updated continuously with each purchase or sale. For example, if physical inventory reveals a shortage, the accounting value of inventory is adjusted accordingly. Both are essential for ensuring accurate financial data and efficient inventory management.
What Are Inventory Valuation Methods?
These are the methods used to determine the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the value of remaining inventory. The choice of method depends on the nature of your business and financial goals, as each method affects reported profits and taxes. Key methods include:
- FIFO (First In, First Out): It assumes the oldest items are sold first. It's suitable during inflation as it reflects actual costs, but may increase taxes due to higher reported profits.
- LIFO (Last In, First Out): It assumes the newest items are sold first. Useful for reducing taxes during price increases, but may provide an inaccurate picture of remaining inventory value, and is not allowed under some international standards like IFRS.
- Weighted Average Cost (WAS): takes the average cost of all available units, providing balance during price fluctuations but less accuracy in determining actual profit.
What Are the Procedures for Fixed Asset Inventory?
Fixed asset inventory (e.g., buildings, equipment, vehicles) requires precise procedures to ensure data accuracy and protect company assets. These steps include:
- Identifying and classifying all fixed assets by type (equipment, furniture, etc.).
- Physically inspecting each asset to verify its existence and condition.
- Financial valuation: Assessing the value of each asset based on purchase cost or current market value.
- Recording data in financial records, documenting any damage or loss.
- Periodic review: Conducting regular inventory counts (annually or semi-annually) to ensure data accuracy
Are you facing challenges in inventory management? Wafeq is here to help! for a smoother and more effective inventory management experience.
Are you facing challenges in inventory management? Wafeq is here to help! for a smoother and more effective inventory management experience.














